You have finally made it to the more difficult parts of the course where the goal is automating bot logins across all available bots.
The topics of this section include the following:
- How it all comes together
- Automated login & captcha bypass
- Database models for bot profiles
- Backend routes
- Frontend template
- Testing
How it all comes together
Here’s a high-level overview of how all components in tornet_scraper integrate:
- In Section 3.1, you set up your development environment to get started.
- In Section 3.2, you learned how to generate proxies for secure connections.
- In Section 3.3, you explored creating APIs for CAPTCHA bypassing, identifying Initial Access Brokers (IABs), and translating data.
These are impressive skills. Now, we’ll cover how these elements combine to manage bot profiles. Here’s how the functionalities work together:
- Proxy Generation: You’ll use the proxy generator to create Tor proxies, which bot profiles need to access the Tor site securely.
- API Management: You’ll leverage API management to add a CAPTCHA API, allowing bots to bypass CAPTCHAs and log in successfully.
- Bot Management:
- Use the interface to create bots by entering their username, password, purpose, and assigned proxy.
- Specify the login URL for the bots.
- Click "Perform Bot Login" to log in all bot accounts and bypass CAPTCHAs automatically.
- After login, the system updates a table to show which accounts have active sessions.
If you run "Perform Bot Login" twice for all accounts, the backend will fetch new sessions. Just because a session is marked as active doesn’t guarantee it’s valid. It’s highly recommended to perform bot login every time you launch the app to ensure active and working sessions.
Automated login & captcha bypass
This topic shouldn’t intimidate anyone, it’s not magic. In earlier sections, we explored bypassing CAPTCHAs using the ChatGPT o3 model, but since the OpenAI API for o3 doesn’t support images, we’ll now use the gpt-4.1 model, which has proven effective for CAPTCHA bypassing in my experience.
Always remember that many AI models prohibit CAPTCHA bypassing for malicious purposes, as it violates their terms of service and may be illegal. In this course, we’re using these models in a controlled environment for educational purposes, ensuring compliance with legal standards. I do not endorse or condone illegal activities with AI models.
On the OpenAI platform, the Playground allows you to experiment with various models. I recommend trying it before proceeding, as newer models may be available by the time you read this. With AI models evolving monthly, a more advanced model for OCR might exist when you tackle this section.
The CAPTCHA bypass process is straightforward:
- Open the login page
- Download the CAPTCHA image
- Resize it to improve readability
- Encode the image as base64 and send it to the AI model with a prompt
- Retrieve the extracted CAPTCHA text
- Use the CAPTCHA text, username, and password to log in
- Obtain the session after a successful login
- Use the session to scrape marketplaces, posts, and profiles
While this may seem complex, breaking it down into individual functions makes it easy to understand how everything connects.
The code for performing login with CAPTCHA bypass is located in app/services/tornet_forum_login.py.
Functions
-
image_to_base64:- Purpose: Converts an image file to a base64-encoded string for API submission.
- Key Parameters:
image_path: Path to the image file.
- Returns: Base64 string or
Noneon error. - Details: Reads the image file in binary mode, encodes it to base64, and logs the process. Returns
Noneif file access or encoding fails.
-
resize_image:- Purpose: Resizes an image to specified dimensions for consistent CAPTCHA processing.
- Key Parameters:
image_path: Path to the input image.output_path: Path to save the resized image.size: Tuple of target dimensions (default: 354x112).
- Returns:
Trueon success,Falseon error. - Details: Uses PIL to resize the image with LANCZOS resampling, saves it as PNG, and logs the operation. Returns
Falseif resizing or saving fails.
-
clean_captcha_text:- Purpose: Extracts a 6-character CAPTCHA code (uppercase letters and numbers) from raw text.
- Key Parameters:
captcha_text: Text output from the OpenAI API.
- Returns: 6-character code or
Noneif extraction fails. - Details: Uses regex (
[A-Z0-9]{6}) to find the code, logs the cleaned result, and returnsNoneif no match is found or an error occurs.
-
solve_captcha:- Purpose: Solves a CAPTCHA image using the OpenAI API.
- Key Parameters:
image_path: Path to the CAPTCHA image.api_key: OpenAI API key.model_name: OpenAI model (e.g., GPT-4).max_tokens: Maximum tokens for the API response.prompt: Instruction text for the API.
- Returns: Cleaned 6-character CAPTCHA code or
Noneon error. - Details:
- Resizes the CAPTCHA image to a fixed size using
resize_image. - Converts the resized image to base64 using
image_to_base64. - Sends the base64 image and prompt to the OpenAI API via
client.chat.completions.create, requesting the CAPTCHA text. - Cleans the API response using
clean_captcha_textand returns the result. Logs errors and returnsNoneon failure.
- Resizes the CAPTCHA image to a fixed size using
-
login_to_tor_website:- Purpose: Logs into a Tor website by solving CAPTCHAs and submitting login credentials, returning a session with cookies.
- Key Parameters:
api_key: OpenAI API key for CAPTCHA solving.max_tokens: Maximum tokens for OpenAI API.model_name: OpenAI model name.login_url: URL of the login page.username: Login username.password: Login password.tor_proxy: Tor proxy URL (e.g.,socks5h://127.0.0.1:9050).prompt: Prompt for OpenAI CAPTCHA solving.timeout: Request timeout (default: 20 seconds).
- Returns:
requests.Sessionwith cookies on success,Noneon failure. - Details:
- Creates a
requests.Sessionwith the Tor proxy and a random user agent (fromgen_desktop_ua). - Attempts login up to 9 times, with a 5-minute wait after max attempts.
- Fetches the login page, extracts the CAPTCHA image URL using BeautifulSoup, and downloads it.
- Solves the CAPTCHA using
solve_captcha. - Submits login data (username, password, CAPTCHA code, and any hidden form fields like CSRF tokens) via POST.
- Checks the response for success (
"profile" and "logout"in text), invalid credentials, or invalid CAPTCHA. Retries on failures, cleans up temporary files (CAPTCHA images), and returns the session with cookies on success.
- Creates a
The script attempts login up to 9 times before pausing for 5 minutes and retrying. CAPTCHA solving can be unpredictable, with some CAPTCHAs being easier to solve than others. The strategy is to persist with retries until a successful login is achieved. Typically, success occurs within 5 attempts based on my experience.
Database models for bot profiles
The database models for bot profiles include all necessary details, such as bot purpose, tornet_forum URL, and bot accounts, but these are organized into separate models for better management and clarity.
Your models are located at app/database/models.py. Here are they:
class BotPurpose(enum.Enum):
SCRAPE_MARKETPLACE = "scrape_marketplace"
SCRAPE_POST = "scrape_post"
SCRAPE_PROFILE = "scrape_profile"
class BotProfile(Base):
__tablename__ = "bot_profiles"
id = Column(Integer, primary_key=True, index=True)
username = Column(String, unique=True, nullable=False)
password = Column(String, nullable=False)
purpose = Column(Enum(BotPurpose), nullable=False)
tor_proxy = Column(String, nullable=True)
user_agent = Column(String, nullable=True)
session = Column(Text)
timestamp = Column(DateTime, default=datetime.utcnow)
BotPurpose defines a bot's primary task, supporting three scraping types:
- Scraping marketplace post links (excluding content).
- Scraping posts with their links.
- Scraping post links from user profiles.
This necessitates distinct bot types for each purpose.
Backend routes
The tornet_forum_login.py module handles the core login functionality, so no unique interactions are needed for it. The bot profile interface requires the following key functionalities:
- Listing existing bots.
- Creating new bots.
- Updating bot details.
- Deleting bots.
- Creating and modifying onion URLs.
- Performing login.
These align with the CRUD operations discussed previously. The login functionality relies on the login_to_tor_website function, so no new concepts are introduced beyond standard CRUD.
Your code is located in app/routes/bot_profile.py.
Functions
-
get_bot_profiles:- Purpose: Retrieves all bot profiles from the database.
- Key Parameters:
db: SQLAlchemySession(viaDepends(get_db)).
- Returns: List of dictionaries with profile details (ID, username, masked password, purpose, Tor proxy, session status, user agent, timestamp).
- Details: Queries the
BotProfiletable, masks the password for security, and returns profile data. RaisesHTTPException(500) on errors.
-
create_bot_profile:- Purpose: Creates a new bot profile.
- Key Parameters:
profile:BotProfileCreatewith profile data.request: FastAPIRequestfor session-based flash messages.db: SQLAlchemySession.
- Returns: Dictionary with success message and flash message.
- Details: Checks for duplicate usernames, creates a
BotProfileinstance with a random user agent (fromgen_desktop_ua), saves it to the database, and adds a success flash message to the session. RaisesHTTPException(400 for duplicates, 500 for errors) with rollback on failure.
-
update_bot_profile:- Purpose: Updates an existing bot profile.
- Key Parameters:
profile_id: Integer ID of the profile.profile:BotProfileUpdatewith updated fields.request: FastAPIRequestfor flash messages.db: SQLAlchemySession.
- Returns: Dictionary with success message and flash message.
- Details: Verifies the profile exists, checks for duplicate usernames (if changed), updates non-
Nonefields (includingBotPurposeenum), and commits changes. Adds a success flash message. RaisesHTTPException(404 if not found, 400 for duplicates, 500 for errors) with rollback on failure.
-
delete_bot_profile:- Purpose: Deletes a bot profile.
- Key Parameters:
profile_id: Integer ID of the profile.request: FastAPIRequestfor flash messages.db: SQLAlchemySession.
- Returns: Dictionary with success message and flash message.
- Details: Verifies the profile exists, deletes it from the
BotProfiletable, and adds a success flash message. RaisesHTTPException(404 if not found, 500 for errors) with rollback on failure.
-
get_onion_url:- Purpose: Retrieves the latest onion URL.
- Key Parameters:
db: SQLAlchemySession.
- Returns: Dictionary with the latest
OnionUrl.urlorNone. - Details: Queries the
OnionUrltable, ordered by timestamp (descending), and returns the most recent URL. RaisesHTTPException(500) on errors.
-
set_onion_url:- Purpose: Creates a new onion URL entry.
- Key Parameters:
onion:OnionUrlCreatewith the URL.request: FastAPIRequestfor flash messages.db: SQLAlchemySession.
- Returns: Dictionary with success message and flash message.
- Details: Creates an
OnionUrlinstance, saves it to the database, and adds a success flash message. RaisesHTTPException(500) with rollback on failure.
-
perform_bot_login:- Purpose: Automates login for all bot profiles using a CAPTCHA API.
- Key Parameters:
request: FastAPIRequestfor flash messages.db: SQLAlchemySession.
- Returns: Dictionary with login results and flash message.
- Details:
- Fetches the latest
OnionUrland activecaptcha_apifrom theAPIstable. - Queries all
BotProfileentries and attempts login for each usinglogin_to_tor_website(fromtornet_forum_login.py) with CAPTCHA API parameters. - If a session cookie is received, formats it as
session=<value>, updates the profile’ssessionfield, and increments success count. Failed logins are logged and collected. - Returns a summary message with success count and failed logins, adding a flash message (success if any logins succeed, error otherwise). Raises
HTTPException(400 for missing URL/API/profiles, 500 for errors) with rollback on failure.
- Fetches the latest
Frontend template
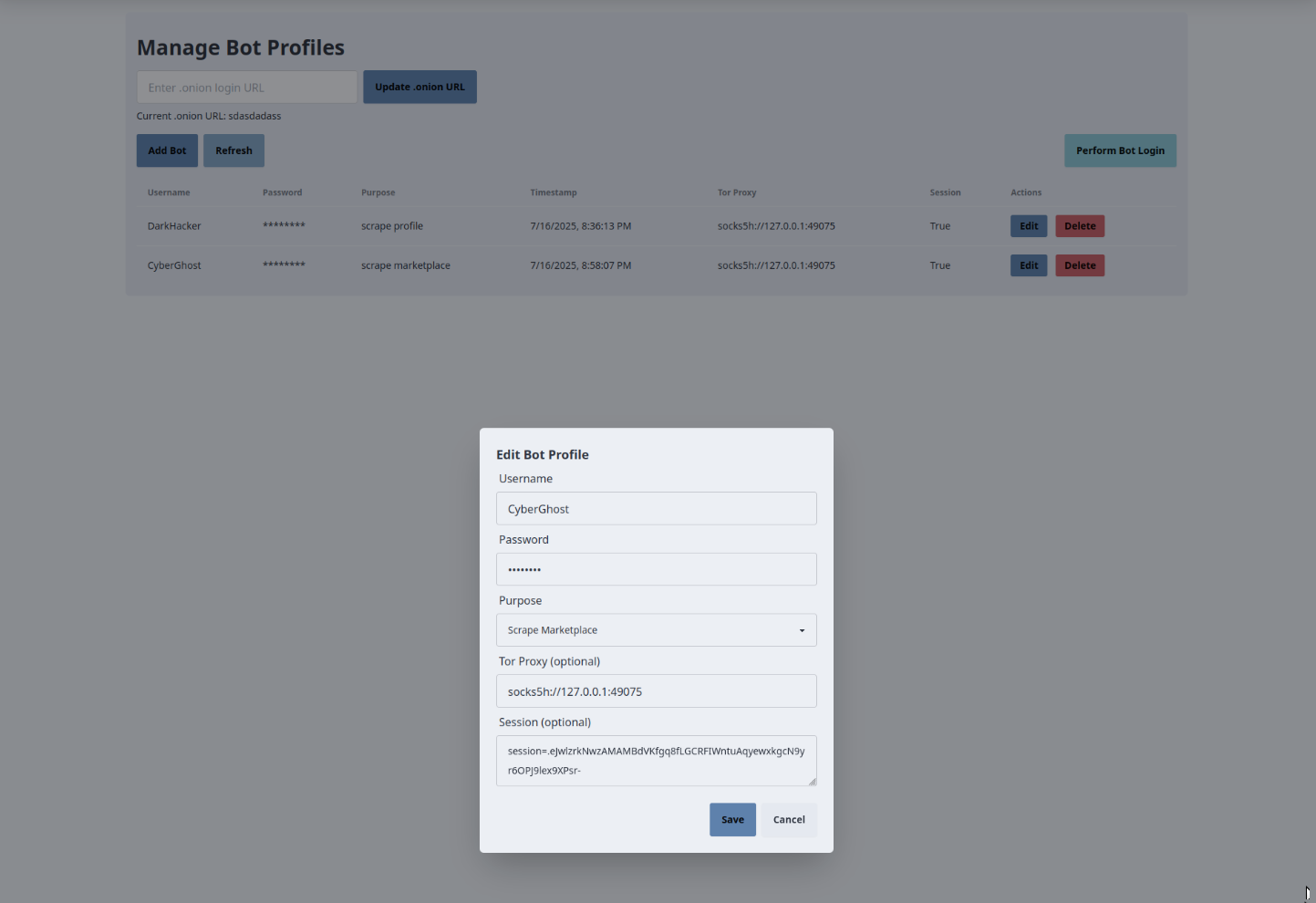
Your template code is located in app/templates/bot_profile.html.
The bot_profile.html template provides a UI for managing bot profiles and onion URLs in the tornet_scraper application, interacting with the backend via API calls to perform CRUD operations on bot profiles, set onion URLs, and automate logins. Below is a concise explanation of its core functionalities and backend interactions.
-
Onion URL Management:
- Purpose: Allows users to set and display the
.onionURL for Tor website access. - Backend Interaction:
- An input field and "Update .onion URL" button trigger
setOnionUrl(), sending an AJAX POST request to/api/bot-profile/onion-url(handled bybot_profile.py::set_onion_url) with the entered URL. - The backend saves the URL to the
OnionUrltable, adds a success flash message to the session, and returns a success response. On success, the page reloads, andloadOnionUrl()fetches the latest URL via a GET request to/api/bot-profile/onion-url, updating the display. Errors trigger an error flash message.
- An input field and "Update .onion URL" button trigger
- Purpose: Allows users to set and display the
-
Bot Profile Creation:
- Purpose: Enables adding new bot profiles.
- Backend Interaction:
- The "Add Bot" button opens a modal with fields for username, password, purpose (dropdown:
scrape_marketplace,scrape_post,scrape_profile), Tor proxy, and session (optional). - The
createBotProfile()function sends an AJAX POST request to/api/bot-profile/create(handled bybot_profile.py::create_bot_profile) with form data. - The backend validates the username, creates a
BotProfilewith a random user agent, saves it to the database, and adds a success flash message. On success, the modal closes, and the page reloads. Errors (e.g., duplicate username) trigger an error flash message.
- The "Add Bot" button opens a modal with fields for username, password, purpose (dropdown:
-
Bot Profile Listing and Updates:
- Purpose: Displays and refreshes a table of bot profiles.
- Backend Interaction:
- The
loadBotProfiles()function, triggered on page load and by the "Refresh" button, sends an AJAX GET request to/api/bot-profile/list(handled bybot_profile.py::get_bot_profiles). - The backend returns a list of profiles (ID, username, masked password, purpose, Tor proxy, session status, user agent, timestamp), populating the table. Errors trigger an error flash message.
- The table updates automatically after create, update, or delete actions.
- The
-
Bot Profile Editing:
- Purpose: Allows updating existing bot profiles.
- Backend Interaction:
- Each table row’s "Edit" button calls
openEditModal(), populating a modal with profile data. - The
updateBotProfile()function sends an AJAX PUT request to/api/bot-profile/{profile_id}(handled bybot_profile.py::update_bot_profile) with updated fields (username, password, purpose, Tor proxy, user agent, session; optional fields can remain unchanged). - The backend validates and updates the
BotProfile, adding a success flash message. On success, the modal closes, and the page reloads. Errors (e.g., duplicate username) trigger an error flash message.
- Each table row’s "Edit" button calls
-
Bot Profile Deletion:
- Purpose: Deletes a bot profile.
- Backend Interaction:
- Each table row’s "Delete" button opens a confirmation modal via
openDeleteModal(), storing the profile ID. - The
deleteBotProfile()function sends an AJAX DELETE request to/api/bot-profile/{profile_id}(handled bybot_profile.py::delete_bot_profile). - The backend deletes the profile from the
BotProfiletable and adds a success flash message. On success, the modal closes, and the page reloads. Errors trigger an error flash message.
- Each table row’s "Delete" button opens a confirmation modal via
-
Automated Bot Login:
- Purpose: Triggers login for all bot profiles using CAPTCHA-solving.
- Backend Interaction:
- The "Perform Bot Login" button calls
performBotLogin(), sending an AJAX POST request to/api/bot-profile/perform-login. - The backend fetches the latest onion URL, active CAPTCHA API, and all profiles, then uses
login_to_tor_websiteto authenticate each profile, storing session cookies in theBotProfiletable. It returns a summary of successful and failed logins with a flash message (success if any logins succeed, error otherwise). - On success or error, the page reloads, and flash messages display the outcome.
- The "Perform Bot Login" button calls
Testing
To test this functionality, you need to first add a Captcha API, I'd recommend getting a gpt-4.1 API key and adding it through API Management page.
For prompt, you could use this:
The attached image is 6 characters, it contains letters and numbers. The letters are all uppercase. I want you to analyze the image and extract the characters for me, send the combined characters as answer.
After everything is done, you should be able to perform login against one or multiple accounts and their sessions will be updated, if session is set to true then it was probably filled out.